Enlightening Journey of Yoga
Yoga means to join i.e to unite the inner consciousness with the universal consciousness which leads to the perfect harmony between body and the soul. The main aim of yoga is Self-realisation, so as to overcome all kind of suffering, which leads to the attainment of Moksha. Now the question which comes in mind is “What is Moksha? Will it be considered as a part of any religion? Can we really achieve it by practising yoga”. Basically answer of all the above questions can be answered by knowing and practising yoga. The main objective of Yoga practice is to live freely in all walks of life including health and harmony. Yoga is science as well an art, practised by human being so as to attain Self-realisation. It is believed that the journey of yoga started with yoga practice during Indus Valley civilisation around 2700 B.C. Practice of Yoga in ancient India was discovered by archaeologist who found many seals and fossils from the remains of Indus valley civilisation having cravings of Yogic objects and figures performing Yoga Sadhana.

( Ref: McEvilley, Thomas (1981). “An Archaeology of Yoga”. RES: Anthropology and Aesthetics. 1: 44–77. JSTOR 20166655.)
During Vedic culture Sun had been given highest importance. Surya namashkar came into practice due to this. Sage Maharshi Patanjali who is considered as “The father of Yoga” compiled 195 sutra which can be used for incorporating Yoga into daily routine which help in living an ethical life. Yoga sutras are the foundation of what we call classical yoga.
Different periods of yoga are
(1) Vedic yoga
(2) Preclassical yoga
(3) Classical Yoga
(4) Post classical yoga
The evidence of vedic yoga can be seen in the four Vedas namely Rig-Veda, Yajurveda, Samaveda and Atharvaveda. Yoga can be considered as an important aspect of vedic scriptures. It is these inspiring text which encourages the practice of yoga to unify the physical realm with the spiritual realm.
We can consider the period when Upanishad, Bhagwat Gita, Ramayana and Mahabharata came into light as the birth of pre classical period of yoga. In Bhagwat Gita, it is mentioned that-

The man whose disposition is disciplined transcends both good and bad actions in this world. Therefore prepare yourself for Yoga. Yoga means great strength in actions.
Yoga practice of pre-classical time was mainly focused on meditation, self-realization and connection with the universal one.
Classical Yoga period was the system of Ashtanga yoga potrayed in the ancient script as the The Yoga sutras of Patanjali.
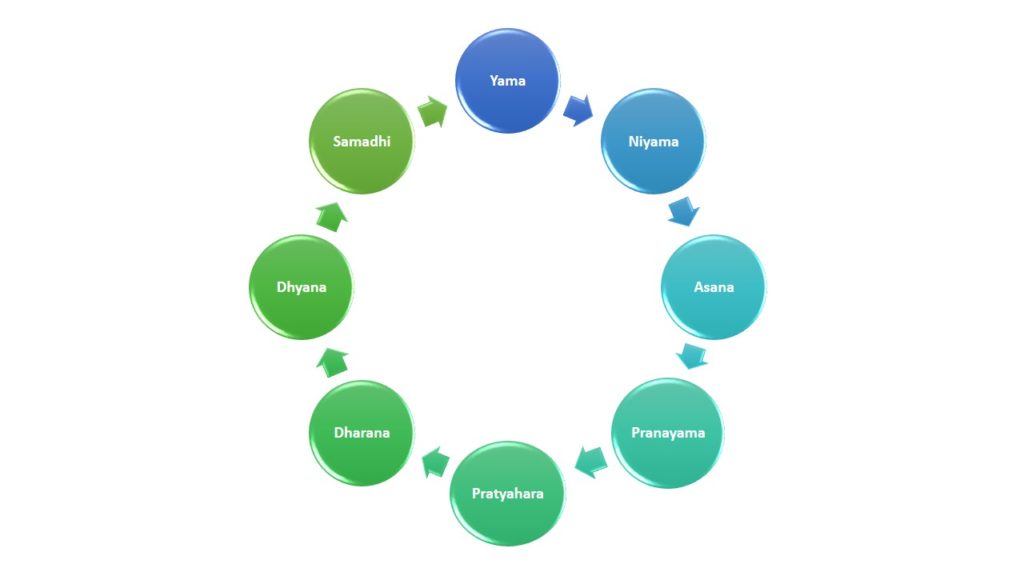
Postclassical yoga period was the one in which physical benefits from yoga was understood and came into practice. It is this time when yogi started to teach yoga in order to heal body and re-energize body for longevity. This practice is called Hatha Yoga. Hatha yoga is the yoga of postures or asanas.
Era of Modern Yoga started when Swami Vivekananda gave speech at World’s Parliament of Religions in 1893 held at Chicago. After this, world gave serious attention to teachings and practice of yoga.
At last, yoga become homonym with traditional as well as modern outlook with the realization through self practice, a union of Jivatma with Paramatama, Shiv with Shakti, Purusha with Prakriti and modern meaning as, wide variety of postures and physical fitness.
Keep Reading !!!



Yoga is good for physic,mind and spirit.